What Is Hepatitis A B C?
October is Liver Cancer Awareness Month. As part of this month, let’s dive into the world of hepatitis or inflammation of the liver. Even though this viral infection is a global health concern, massive vaccination and screening efforts have caused hepatitis rates to drop significantly.
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is an essential organ since it does several things for the body, including the breakdown of nutrients and blood filtration. If anything happens to the liver, the body can have severe problems functioning normally.
While some lifestyle behaviors, such as heavy alcohol compensation, can cause liver damage, hepatitis is caused by the hepatitis virus. There are five types of hepatitis: hepatitis A, hepatitis, B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, and hepatitis E. In America, the most commonly seen types of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, and C.
It is important to note that the hepatitis viruses have existed for many years and have infected millions of people. If left untreated, hepatitis B and C can lead to deadly complications and a potential risk for liver cancer later in life.
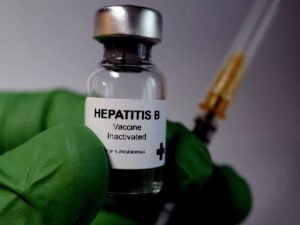
Since the release of hepatitis vaccines, hepatitis rates in America and around the world have decreased. However, with a growing population hesitant towards vaccines, nurses and other health care professionals need to be aware of this serious infection.